备忘:
export JAVA_HOME=/jdk1.8.0_211
export JRE_HOME=/jdk1.8.0_211/jre
export CLASS_PATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JRE_HOME/lib
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin:$PATH
备忘:
export JAVA_HOME=/jdk1.8.0_211
export JRE_HOME=/jdk1.8.0_211/jre
export CLASS_PATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JRE_HOME/lib
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JRE_HOME/bin:$PATH
1.下载文件:
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.2.0.tar.gz
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.2.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.2.0.tar.gz
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/packs/x-pack/x-pack-5.2.0.zip
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/heartbeat/heartbeat-5.2.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.2.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/packetbeat/packetbeat-5.2.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
2.分别解压elasticsearch\kibana\logstash后,各自执行以下命令安装xpack。
bin/elasticsearch-plugin install file:///path/to/file/x-pack-5.2.0.zip
bin/kibana-plugin install file:///path/to/file/x-pack-5.2.0.zip
bin/logstash-plugin install file:///path/to/file/x-pack-5.2.0.zip
卸载命令
bin/elasticsearch-plugin remove x-pack
bin/kibana-plugin remove x-pack
bin/logstash-plugin remove x-pack
3.启动相应应用
bin/elasticsearch
bin/kibana
bin/logstash
4.登录相关后台
----------------------------
kibana的后台:
http://localhost:5601
帐号与密码
Username: elastic Password: changeme
------------------------------
elasticsearch的restfullAPI
http://localhost:9200
-----------------------
logstash的后台
参考文档:
https://www.elastic.co/start
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/x-pack/current/xpack-introduction.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/x-pack/current/installing-xpack.html
1.下载合适的solr版本。当前官网最新版本是6.4.1,但经验证,6.4.1版本在其管理后台中操作dataimport时,会显示空白页。故本人不建议使用最新版本进行学习和应用开发。经验证,其5.5.3版本的各项功能是可以正常工作的。
下载5.5.3版本,快捷路径是:https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/lucene/solr
http://lucene.apache.org/solr/mirrors-solr-latest-redir.html
选择任意一个镜像,在进入镜像后,选择parent目录。
选择5.5.3的版本:https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/lucene/solr/5.5.3/
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/lucene/solr/5.5.3/solr-5.5.3.zip
2.如下是其目录结构,初学者,应该习惯阅读Readme.txt文件,该文件记录了一些基本使用操作,很方便学习。
3.内置了几个例子,需要使用特殊命令开启,初学者应该每个例子都体验一下。
bin/solr -e where is one of:
cloud : SolrCloud example
dih : Data Import Handler (rdbms, mail, rss, tika)
schemaless : Schema-less example (schema is inferred from data during indexing)
techproducts : Kitchen sink example providing comprehensive examples of Solr features
4.体验dih例子。
bin/solr -e dih
5.打开管理后台页面:
在实际测试过程中,发现在window中,dataimport等一些相关操作,会失败。只有linux的才会成功,具体原因没有去分析。
http://mysql.mvware.com:8983/solr/
6.logging界面,当执行dataimport或其它操作,如果有错误或执行失败,可以检查该日志信息。
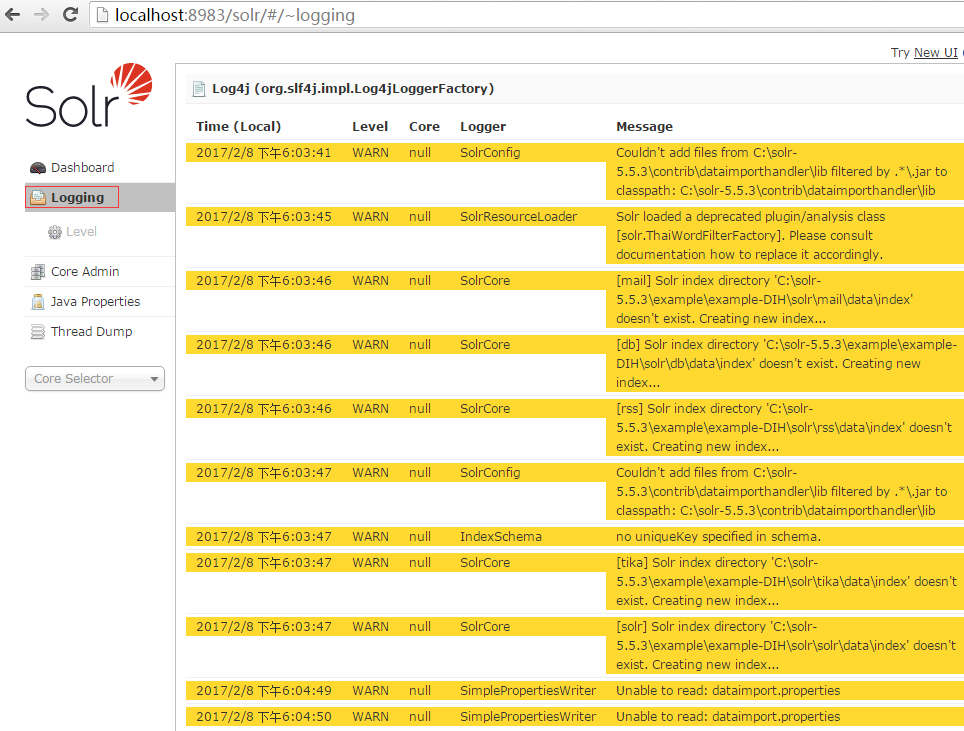
7.在CoreSelector中选择solr项,并选择dataimport项.
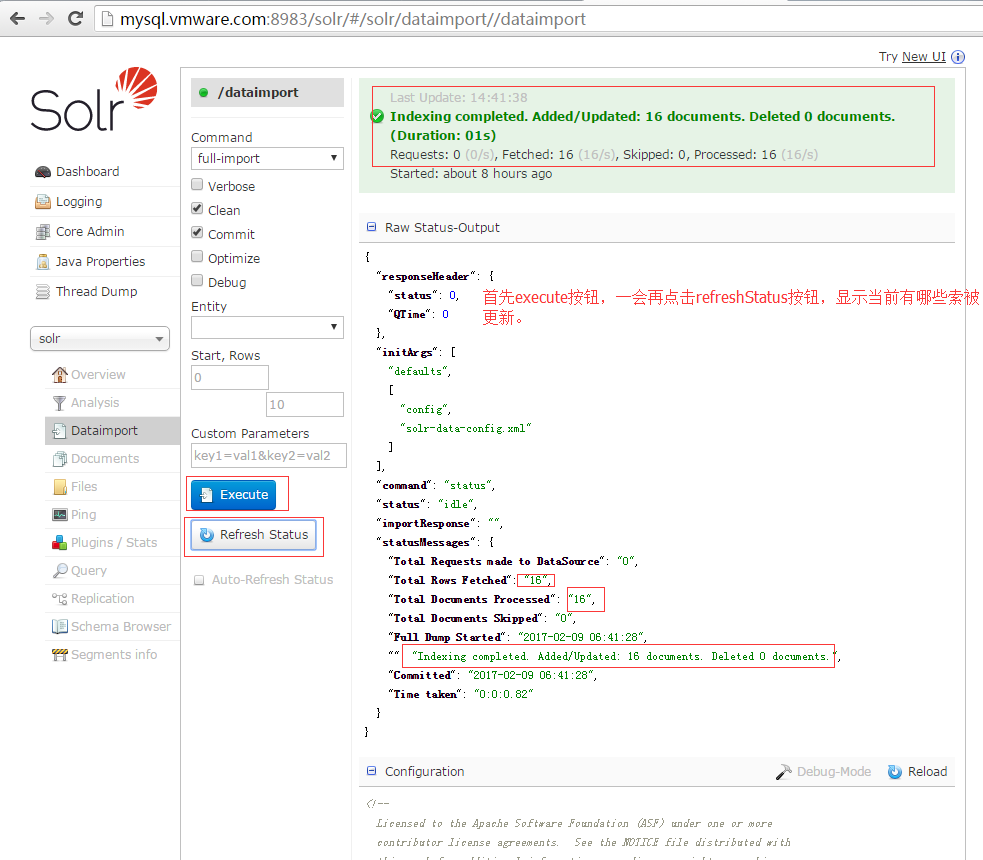
8.在dataimport项中,调试你的配置文件,经过该步骤,已经可以在query项和schemabrowser项中查询到相关记录了。
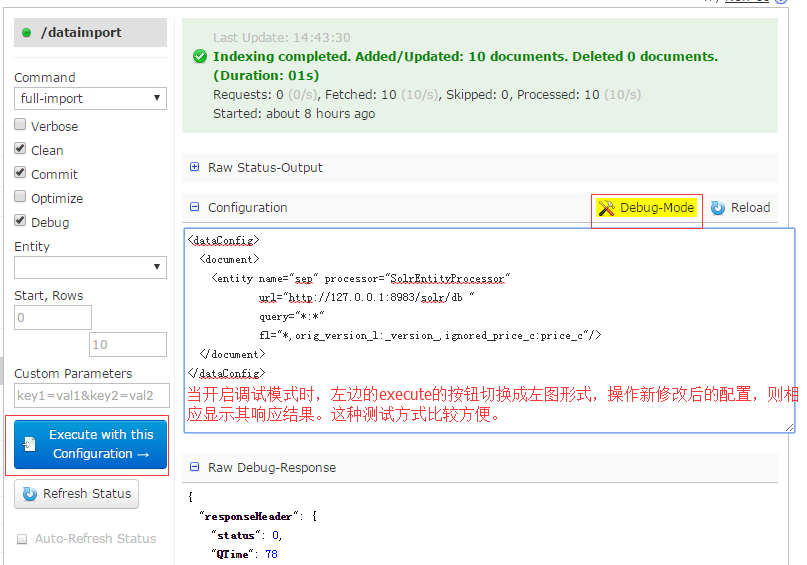
9.在dataimport项中,执行全量更新和增量更新,dataimport项是需要在solrconfig.xml中配置的。
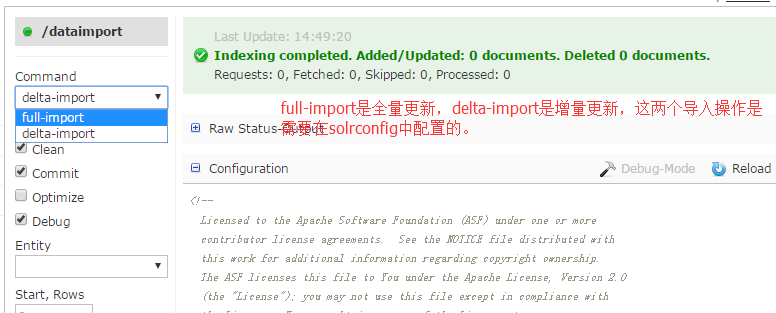
solrconfig.xml中的requestHandler配置
solr-data-config.xml
solr-data-config.xml中的配置
10.浏览schemabrowser中的各个schema项,在solr6.x版本中,增加了schema的增删项,更方便从零搭建core项。
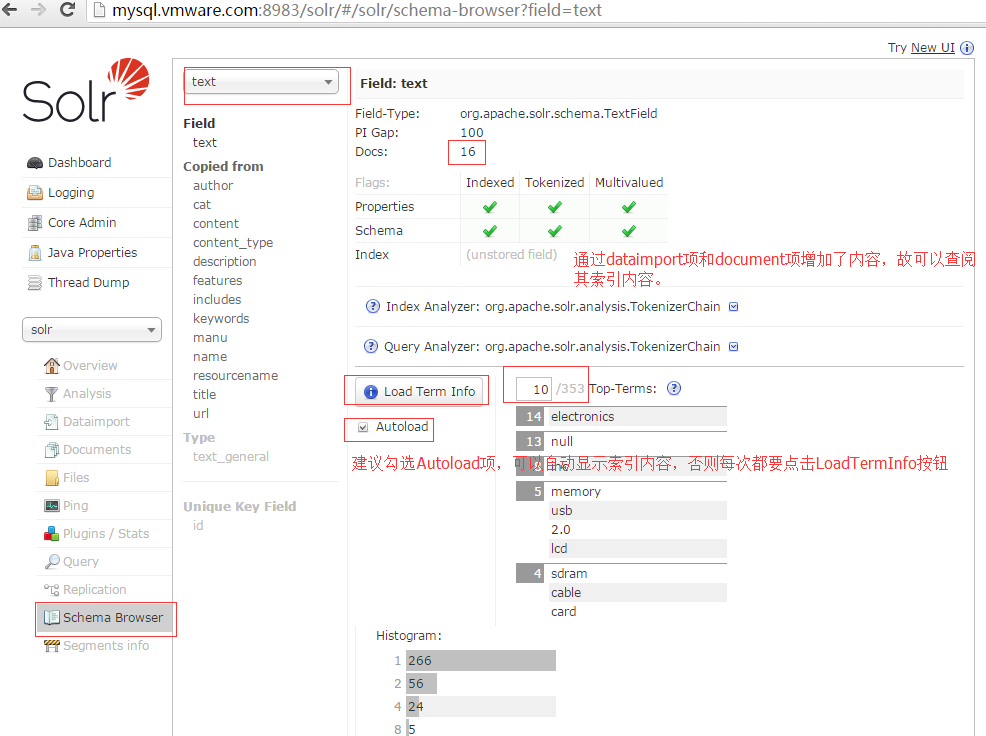
11.通过documents项,增加数据记录,通过schemabrowser或manage-schema.xml配置文件中可知道当前的schema有如下:。
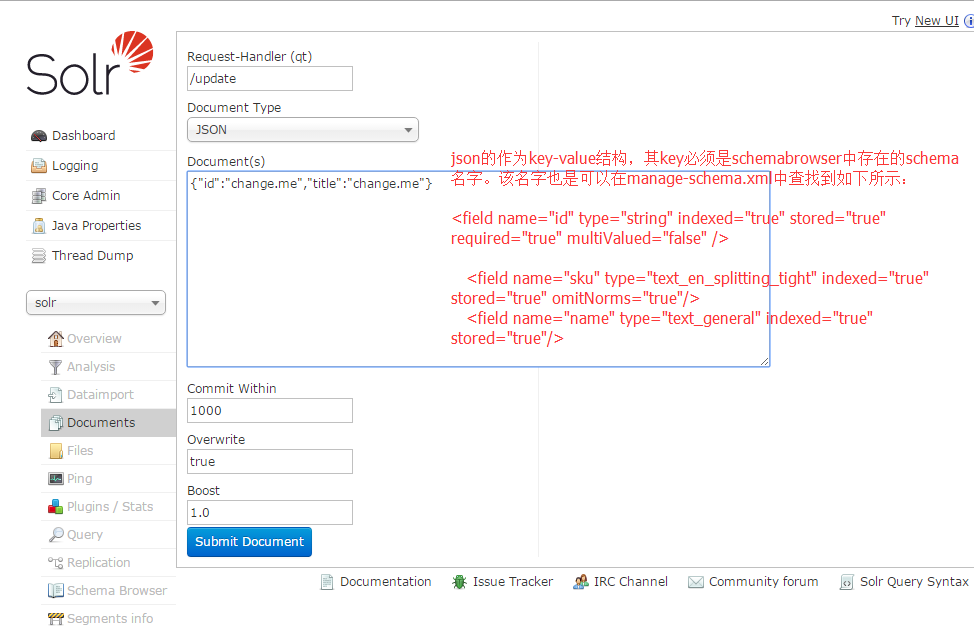
在DocumentType选择JSON项,然后输入内容如下,并点击submit按钮提交:
{"id":12345, "author":"author_121","text":"text_121", "title":"title_1121"}
{"id":22345, "url":"url_121"}
如果执行成功,则提示如下:
Status: success
Response:
{
"responseHeader": {
"status": 0,
"QTime": 2
}
}
如果出错呢?也会有相应的错误提示,可依据提示进行修改输入项内容。

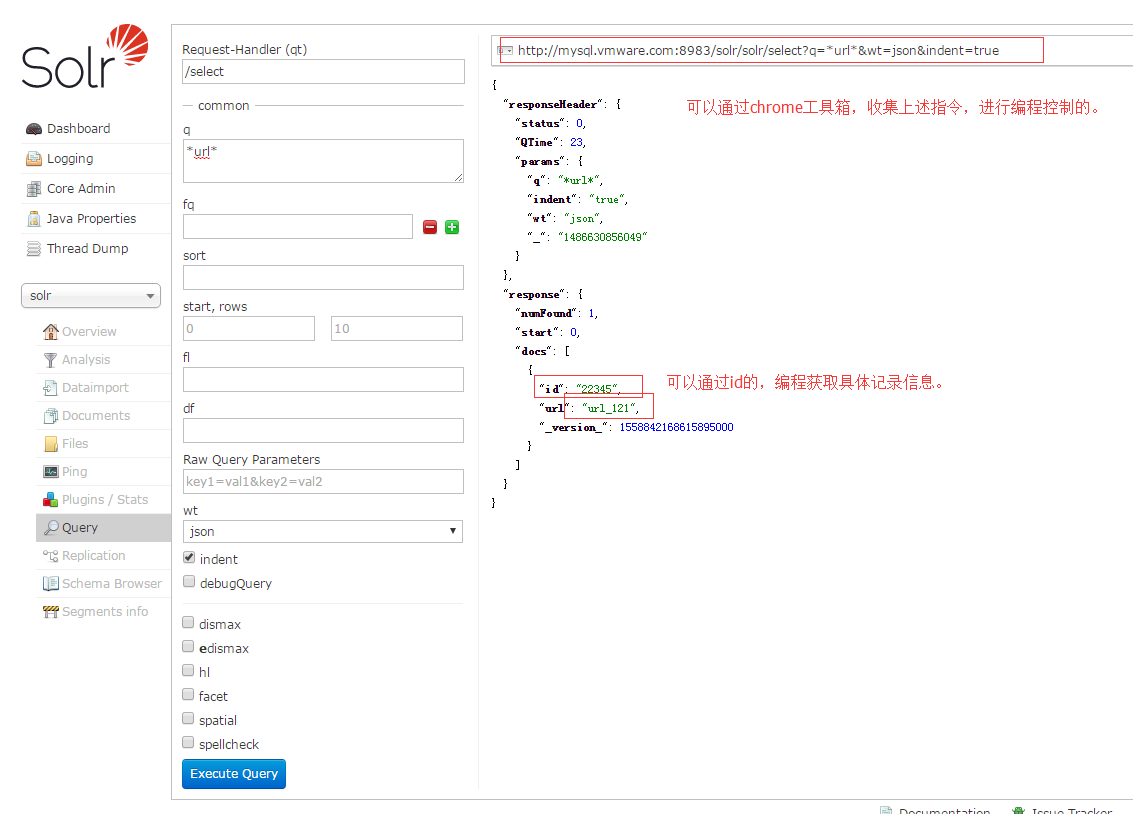
12.通过query项,进行查找刚才的输入项。
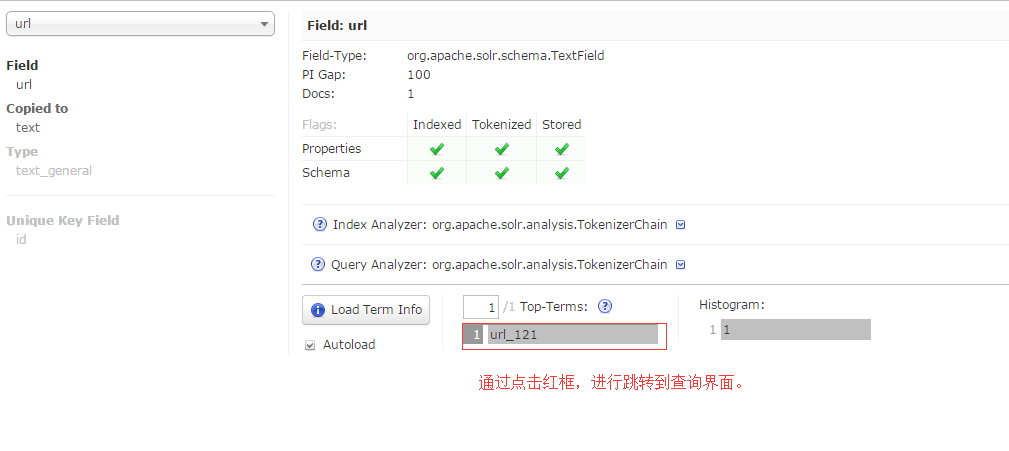
13.也可以通schemabrowser中的记录,快速跳转搜索的内容。
String applicationConfig = "consumer-applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(applicationConfig);
UserInfoService userInfoService = (UserInfoService) context.getBean("userInfoService");
//负载均衡的处理是一个典型的懒加载模式,只有在第一次调用接口时,才进行负载均衡的处理。
System.out.println(userInfoService.sayHello("zhangsan"));
1.在进入sayHello的调用时,堆栈信息和帧代码如下
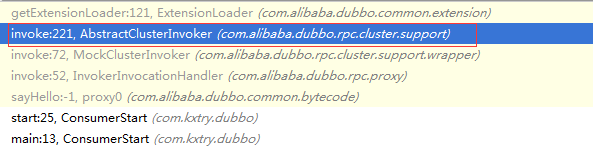
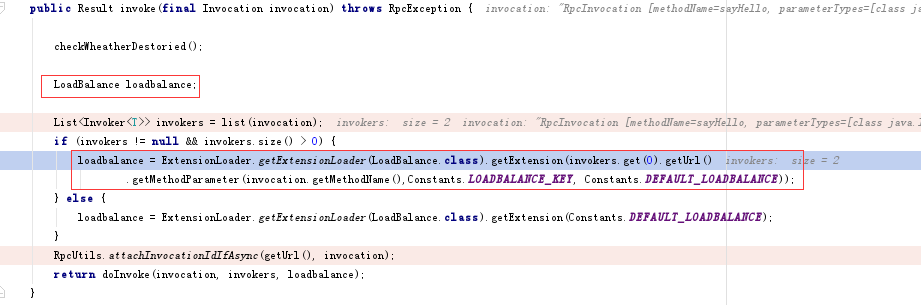
其中Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY的值是“loadbalance”,而Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE的值是“random”,每个接口(reference)均可以灵活配置一个均衡方式,默认不配置的情况下都是random的。
不配置loadbalance时,是random的模式。
2.假如当前的loadbalance设置了leastactive时,它是如何把名字和类LeastActiveLoadBalance的实例关联起来呢?
3.首先它在com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.loadbalance目录下实现了4种均衡方式,如下:
ConsistentHashLoadBalance:一致哈希
LeastActiveLoadBalance:最久不使用
RandomLoadBalance:随机
RoundRobinLoadBalance:顺序循环
注:上1点中的loadbalance返回的则是上述的其中一个均衡策略类实例。
4.其它dubbo实现了一套类似spi的服务加载机制如下:


private void loadFile(Map> extensionClasses, String dir) {
String fileName = dir + type.getName();
try {
Enumeration urls;
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
if (urls != null) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
java.net.URL url = urls.nextElement();
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream(), "utf-8"));
try {
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
final int ci = line.indexOf('#');
if (ci >= 0) line = line.substring(0, ci);
line = line.trim();
if (line.length() > 0) {
try {
String name = null;
int i = line.indexOf('=');
if (i > 0) {
name = line.substring(0, i).trim();
line = line.substring(i + 1).trim();
}
if (line.length() > 0) {
Class clazz = Class.forName(line, true, classLoader);
if (! type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class "
+ clazz.getName() + "is not subtype of interface.");
}
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
if(cachedAdaptiveClass == null) {
cachedAdaptiveClass = clazz;
} else if (! cachedAdaptiveClass.equals(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("More than 1 adaptive class found: "
+ cachedAdaptiveClass.getClass().getName()
+ ", " + clazz.getClass().getName());
}
} else {
try {
clazz.getConstructor(type);
Set> wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (wrappers == null) {
cachedWrapperClasses = new ConcurrentHashSet>();
wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
}
wrappers.add(clazz);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
clazz.getConstructor();
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
name = findAnnotationName(clazz);
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
if (clazz.getSimpleName().length() > type.getSimpleName().length()
&& clazz.getSimpleName().endsWith(type.getSimpleName())) {
name = clazz.getSimpleName().substring(0, clazz.getSimpleName().length() - type.getSimpleName().length()).toLowerCase();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + url);
}
}
}
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name);
if (names != null && names.length > 0) {
Activate activate = clazz.getAnnotation(Activate.class);
if (activate != null) {
cachedActivates.put(names[0], activate);
}
for (String n : names) {
if (! cachedNames.containsKey(clazz)) {
cachedNames.put(clazz, n);
}
Class c = extensionClasses.get(n);
if (c == null) {
extensionClasses.put(n, clazz);
} else if (c != clazz) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate extension " + type.getName() + " name " + n + " on " + c.getName() + " and " + clazz.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("Failed to load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class line: " + line + ") in " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
exceptions.put(line, e);
}
}
} // end of while read lines
} finally {
reader.close();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class file: " + url + ") in " + url, t);
}
} // end of while urls
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", description file: " + fileName + ").", t);
}
}
5.每个均衡策略类均实现了select接口,通过该接口从多个可用的后端服务中返回其中一个服务。
Invoker select(List> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException;
1.Dubbo的客户端请求配置和调用代码如下:
String applicationConfig = "consumer-applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(applicationConfig);
注:在上一文章,曾介绍xml表的命名空间间解析过程,而dubbo:service是服务端配置,而dubbo:reference是客户端配置。
2.构造beanmap列表时,每一行dubbo::refence对应一个ReferenceBean配置。Reference会创建三个对象,如下:
FailoverClusterInvoker:失败转移使用,如服务器宕机等,是从com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Node接口派生的。
MockClusterInvoker:如其名,接口集群化,同一个接口,存在多个服务器为其提供服务支持时,需要一个均衡策略地访问这些服务器。
InvokerInvocationHandler:这个接口是真正的动态代理,它是从InvocationHandler中派生出来的,Failover和MockCluster都是从Node接口派生,用于管理集群的。
3.如下调用代码
UserInfoService userInfoService = (UserInfoService) context.getBean("userInfoService");
System.out.println(userInfoService.sayHello("zhangsan"));
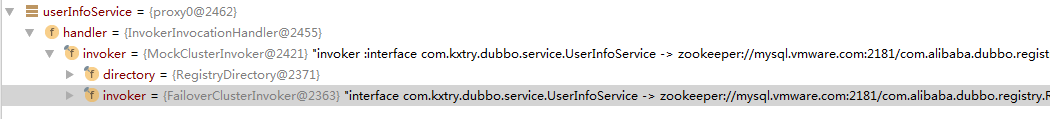
4.如下代码,通过元数据RpcInvocation打包函数名和函数参数,然后通过RPC通信把请求发送到服务器端。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
在Spring中的applicationContext.xml经常看到如下标签
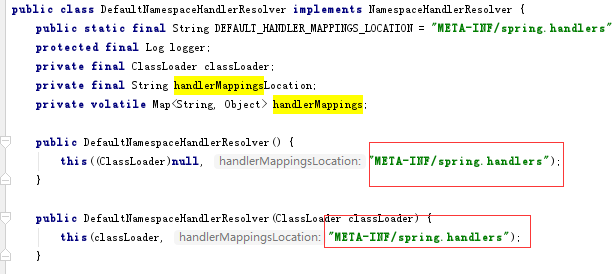
1.Dubbo创建了一个dubbo.xsd文件。
2.并为dubbo.xsd创建了另外两个文件:spring.handlers和spring.schemas(这是Spring的命名解析规范要求),Spring在解析过程中会主动搜索这两资源文件。
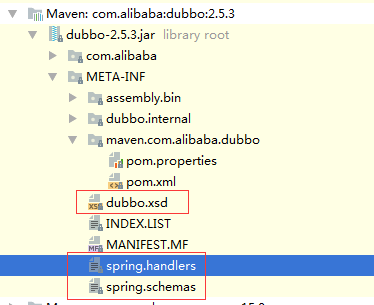
3.spring.handlers文件内容如下
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
4.spring.schemas文件内容如下
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/dubbo.xsd
5.在执行下面代码时,会主动触发相关文件解析。
String configure = "provider-applicationContext.xml";
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configure);
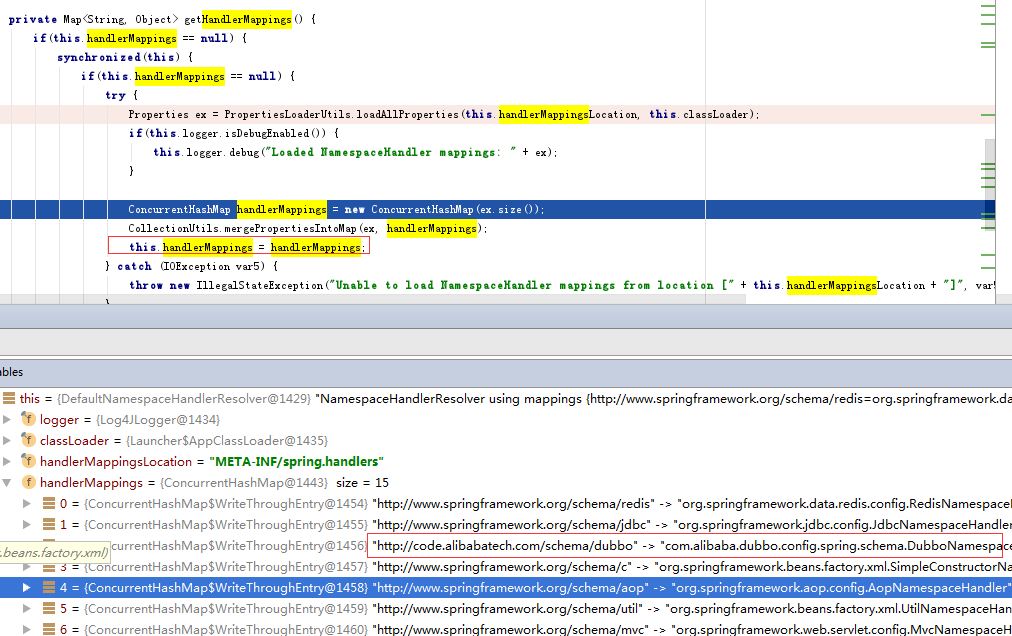
6.具体如下:
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(AnnotationBean.class, true));
}
}
7.上述步骤,已经完成了beanmap列表的建立,但仍需要下述代码,触发Dubbo的建立RPC服务,其中xxxConfig是在xxxBean之前先创建的。
context.start();
context.registerShutdownHook();
8.在6步骤中的的ServiceBean中监听了ApplicationEvent如下:
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (ContextRefreshedEvent.class.getName().equals(event.getClass().getName())) {
if (isDelay() && ! isExported() && ! isUnexported()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("The service ready on spring started. service: " + getInterface());
}
会把xxxConfig的内容,初始化ServiceBean里的对象。
export();
}
}
}
9.serviceBean是多个的,每个service对象,对应一个,故每个对象都监听了ApplicationEvent。
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-23464606-id-4951847.html
http://litaotao.blog.51cto.com/6224470/1301509?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral
看到论坛中的一段介绍,感觉豁然开即朗的感觉,简单总结一下:
从个人感觉:外网IP就是真实IP,而内网IP或局域网IP就是虚拟IP。
以下是摘录别人的:
动态 IP 、固定 IP 、实体 IP 与虚拟 IP都讲解一下,加深理解和知识扩展
实体 IP:在网络的世界里,为了要辨识每一部计算机的位置,因此有了计算机 IP 位址的定义。一个 IP 就好似一个门牌!例如,你要去微软的网站的话,就要去『 207.46.197.101 』这个 IP 位置!这些可以直接在网际网络上沟通的 IP 就被称为『实体 IP 』了。
虚拟 IP:不过,众所皆知的,IP 位址仅为 xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 的资料型态,其中, xxx 为 1-255 间的整数,由于近来计算机的成长速度太快,实体的 IP 已经有点不足了,好在早在规划 IP 时就已经预留了三个网段的 IP 做为内部网域的虚拟 IP 之用。这三个预留的 IP 分别为:
A级:10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
B级:172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
C级:192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
上述中最常用的是192.168.0.0这一组。不过,由于是虚拟 IP ,所以当您使用这些地址的时候﹐当然是有所限制的,限制如下:
私有位址的路由信息不能对外散播
使用私有位址作为来源或目的地址的封包﹐不能透过Internet来转送
关于私有位址的参考纪录(如DNS)﹐只能限于内部网络使用
由于虚拟 IP 的计算机并不能直接连上 Internet ,因此需要特别的功能才能上网。不过,这给我们架设IP网络做成很大的方便﹐比如﹕即使您目前的公司还没有连上Internet﹐但不保证将来不会啊。如果使用公共IP的话﹐如果没经过注册﹐等到以后真正要连上网络的时候﹐就很可能和别人冲突了。也正如前面所分析的﹐到时候再重新规划IP的话﹐将是件非常头痛的问题。这时候﹐我们可以先利用私有位址来架设网络﹐等到真要连上intetnet的时候﹐我们可以使用IP转换协定﹐如 NAT (Network Addresss Translation)等技术﹐配合新注册的IP就可以了。
固定 IP 与 动态 IP:基本上,这两个东西是由于近来网络公司大量的成长下的产物,例如,你如果向中华电信申请一个商业型态的 ADSL 专线,那他会给你一个固定的实体 IP ,这个实体 IP 就被称为『固定 IP 』了。而若你是申请计时制的 ADSL ,那由于你的 IP 可能是由数十人共同使用,因此你每次重新开机上网时,你这部计算机的 IP 都不会是固定的!于是就被称为『动态 IP』或者是『浮动式IP』。基本上,这两个都是『实体IP』,只是网络公司用来分配给用户的方法不同而产生不同的名称而已
@Resource
private ApplicationContext context;
private Environment env;
@Resource的作用相当于@Autowired,只不过@Autowired按byType自动注入,而@Resource默认按 byName自动注入罢了。@Resource有两个属性是比较重要的,分是name和type,Spring将@Resource注解的name属性解析为bean的名字,而type属性则解析为bean的类型。所以如果使用name属性,则使用byName的自动注入策略,而使用type属性时则使用byType自动注入策略。如果既不指定name也不指定type属性,这时将通过反射机制使用byName自动注入策略。
@Resource装配顺序
1. 如果同时指定了name和type,则从Spring上下文中找到唯一匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常
2. 如果指定了name,则从上下文中查找名称(id)匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常
3. 如果指定了type,则从上下文中找到类型匹配的唯一bean进行装配,找不到或者找到多个,都会抛出异常
4. 如果既没有指定name,又没有指定type,则自动按照byName方式进行装配;如果没有匹配,则回退为一个原始类型进行匹配,如果匹配则自动装配;